Understanding Insecticides for Rice Bug: A Comprehensive Guide

The agricultural sector is pivotal in feeding the global population, and rice serves as a staple food for billions of people worldwide. However, rice cultivation faces significant challenges, particularly from pests like the rice bug. The efficient management of these pests is crucial for healthy rice production, and one of the most effective means of control is through the use of insecticide for rice bug. In this article, we will delve deep into the various options available, their effectiveness, and how to use them responsibly in your farming practices.
The Importance of Rice Farming
Rice farming is not just a livelihood for many farmers worldwide; it is essential for food security and economic stability in numerous countries. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), rice provides 20% of the calories consumed globally. Thus, maintaining the health of rice crops is vital. The primary threats to rice production come from insect pests, leading to significant yield losses if not properly managed.
Common Pests Affecting Rice Crops
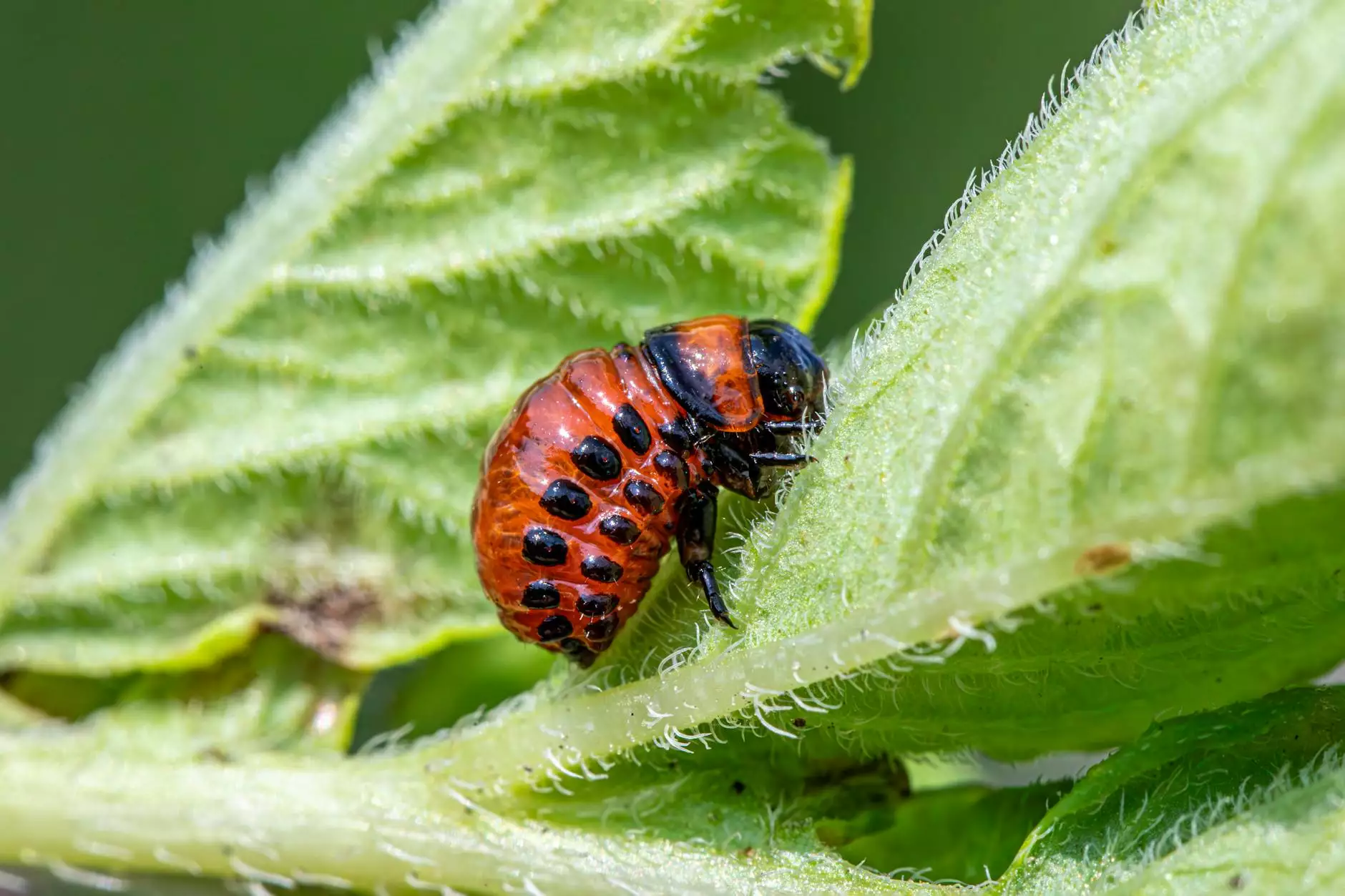
- Rice Bug (Oryztephilus surinamensis)
- Armyworms
- Leafhoppers
- Rice Weevil
- Cutworms
Among these, the rice bug is particularly notorious for its destructive potential. Its feeding habits can lead to substantial losses in yield, making it imperative for farmers to act proactively and implement pest control measures.
What is an Insecticide for Rice Bug?
Insecticides are chemical substances used to kill or control insects and are vital in managing pests like the rice bug. There are various formulations of insecticides, tailored to different needs, crop types, and pest life cycles. For effective management, it is essential to understand the specific characteristics of the insecticide you are considering, including its mode of action, application methods, and potential environmental impact.
Types of Insecticides for Rice Bug Control
When selecting an insecticide for rice bug, farmers have several options available. Here are the primary categories:
1. Synthetic Insecticides
Synthetic insecticides are chemically manufactured and designed to target specific pests effectively. They can be categorized into several classes based on their mode of action:
- Organophosphates: These disrupt the nervous system of the insects. Examples include Chlorpyrifos and Malathion.
- Pyrethroids: These are popular for their low toxicity to humans and mammals. Examples are Permethrin and Cypermethrin.
- Neonicotinoids: These affect the insect's nervous system and are highly effective against a wide range of pests. Imidacloprid is a common example.
2. Biological Insecticides
These include natural substances derived from organisms or naturally occurring compounds. They tend to be less harmful to non-target species and the environment. Some examples include:
- Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt): A naturally occurring bacterium that targets specific insects.
- Neem Oil: Derived from the seeds of the neem tree, it disrupts insect growth and development.
3. Organic Insecticides
Ideal for sustainable farming practices, organic insecticides are made from natural sources and are typically less harmful. Farmers can choose from a variety of options, including:
- Pyrethrum: Derived from chrysanthemum flowers, effective against various pests including rice bugs.
- Insecticidal Soap: Effective in controlling soft-bodied pests through suffocation.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Insecticide
Selecting the right insecticide for rice bug involves several considerations:
- Pest Identification: Knowing your enemy is crucial. Proper identification allows for targeted treatments.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the resistance of local insect populations and potential side effects on beneficial insects.
- Application Method: Different insecticides have different application requirements, whether it be foliar sprays, soil treatments, or pest traps.
- Phytotoxicity: Ensure that the selected insecticide is safe for the crops you are treating to avoid damage.
Best Practices for Using Insecticides
To ensure the effectiveness of your chosen insecticide for rice bug while minimizing risks, adhere to the following best practices:
- Follow Label Instructions: Always read and comply with the manufacturer's labels. This includes application rates, safety precautions, and pre-harvest intervals.
- Integrate Pest Management: Combine chemical treatments with non-chemical practices, such as crop rotation and biological controls, for a holistic approach.
- Monitor Pest Populations: Regularly assess pest populations and crop health to make informed decisions on when and what to apply.
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate protective gear when handling or applying insecticides.
Risks of Overusing Insecticides
While insecticides can be a vital tool, over-reliance can lead to significant challenges, including:
- Pest Resistance: Pests can develop resistance to certain insecticides over time, making them less effective.
- Environmental Damage: Overapplication can harm beneficial insects, disrupt ecosystems, and contaminate water sources.
- Health Risks: Improper handling or excessive use can pose health risks to humans and animals.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Insecticides in Rice Farming
Several regions have successfully implemented effective pest management strategies using insecticide for rice bug:
- Vietnam: Farmers have successfully employed a combination of pyrethroids and biological controls, resulting in up to a 30% increase in yield.
- India: The integrated pest management approach has led to lower pesticide use and increased biodiversity in rice-growing regions.
- Thailand: The use of neem oil as a natural insecticide has reduced chemical dependency while maintaining pest control effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing rice bugs effectively is critical for sustainable rice production. By utilizing the right insecticide for rice bug while implementing integrated pest management practices, farmers can safeguard their crops and ensure robust yields. Continuous education and adaptation to best practices will play a key role in fostering a resilient agricultural sector. Remember that the choices we make in pest management not only impact our immediate harvests but also the long-term health of our ecosystems.
For more insights and products related to farming equipment and pest control, explore our offerings at tsgcinc.com.